Design thinking has revolutionised the business world, helping corporations cope during a time where problems are becoming increasingly complex, and processes elaborate. According to Juliana Goh, the founder of Unigons X Design Consultancy, design thinking goes beyond a designer’s tool to become an “industry agnostic,” a framework applicable for any and all. It’s a mindset that emphasises on user-centricity and co-creation. Thanks to this methodology, teams can work dynamically, drive innovation, creativity, and success.
Design Thinking
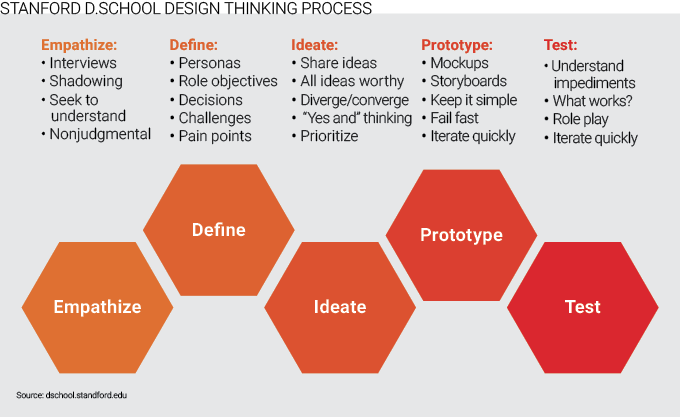
Design thinking, while versatile in its definitions, is a robust methodology capable of driving cultural shifts. It is structured around the 5Ds: Discover, Define, Design, Develop, Deliver, with time allocations strategically balanced of 30%, 20%, 20%, 20%, and 10% respectively.
Why this specific allocation? The “Discover” phase, often overlooked, is pivotal for accurately identifying customer challenges. Dedicating 30% of the time to this initial stage ensures thorough understanding and prevents misdirected efforts later on. Properly identifying the problem areas not only conserves resources but also uncovers existing gaps and opportunities, enabling the creation of solutions that effectively address unmet needs.
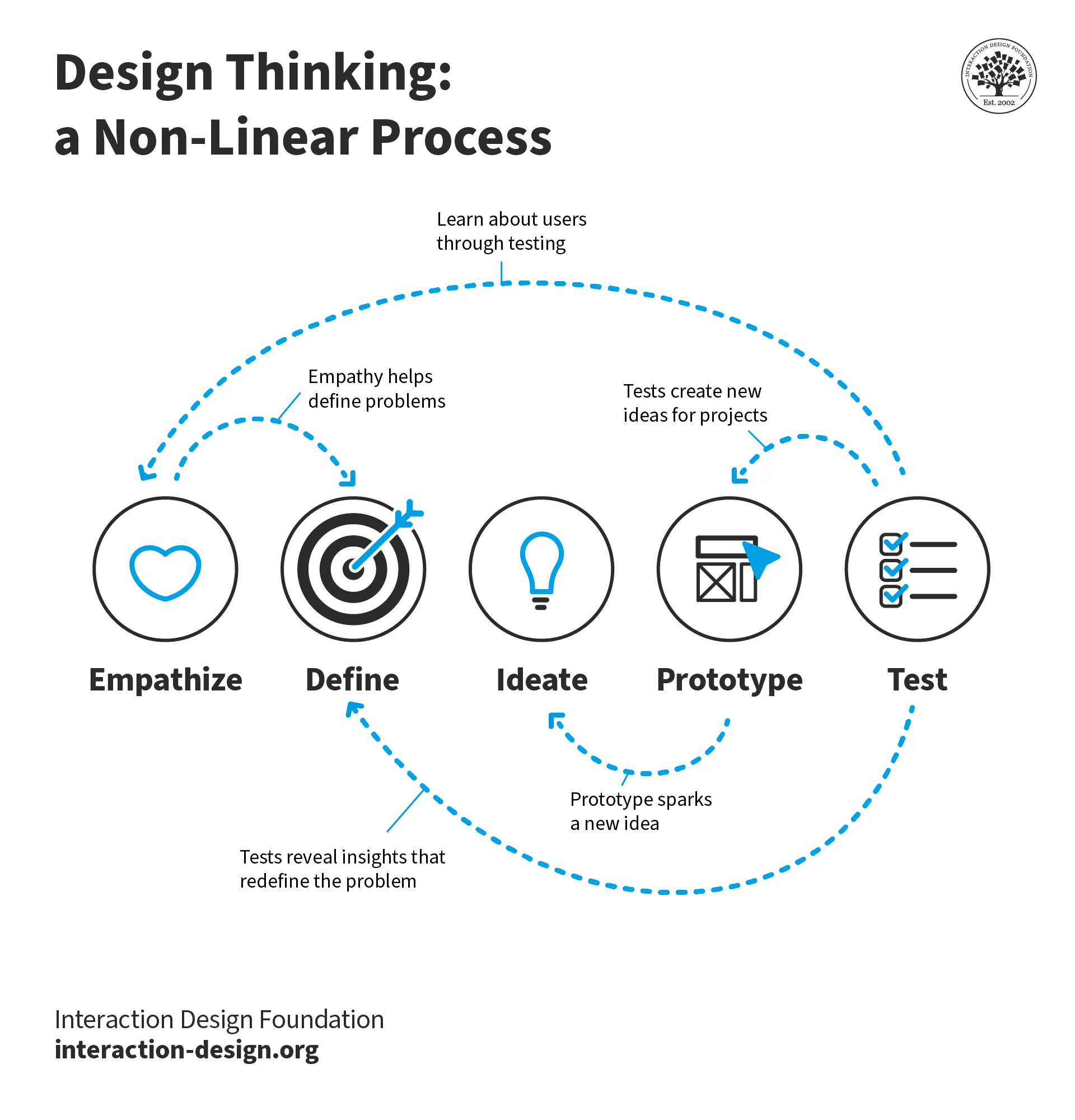
A popular alternative version of Design Thinking
Design Thinking is guided by these key principles:
- Customer Centricity: Ensure products are valuable and relevant by helping users achieve their goals.
- Collaboration and Co-creation: Foster cross-collaboration and align with stakeholders, real users, clients, and tech teams to solve design problems and create genuine products.
- Testing and Iterating: Develop prototypes to test with real users, iterate to improve, and innovate by transitioning the product into the digital realm.
Each phase of Design Thinking is supported by a variety of tools and resources. These tools guide us in maintaining user-centricity, facilitating cross-collaboration, and fostering alignment across teams and departments.
Journey Mapping is a powerful tool that allows us to visualize and understand the customer or user experience as they interact with a company, product, or service over time. This process helps organizations identify pain points, moments of delight, and opportunities for improvement within the customer journey. By pinpointing where and how customers engage with the brand, Journey Mapping enables us to gauge customer satisfaction and recognize emotional highs and lows, ultimately guiding strategic enhancements to the overall experience.
Case studies
The success stories of DBS and KPMG epitomize the transformative power of design thinking in business innovation.
In Jakarta, DBS Bank faced a sharp decline in customer traffic. To address this, the bank aimed to enhance its’ bank customer experience. Through interviews with 15 relationship managers and 15 valued clients, DBS identified the core issue: relationship managers (RMs) were frequently tasked with concierge services to meet the expectations of frequently traveling clients. This responsibility consumed the RMs’ time, hindering their ability to conduct necessary research and limiting client visits to just once a year.
This discovery revealed that simply redesigning the customer experience would not resolve the bank’s challenges. Engaging in a co-creation effort with relationship managers (RMs), the team used an impact-effort prioritization matrix to prioritize ideas. This process led to proposed solutions such as self-help escort services and AI-powered e-butler services. These innovations aimed to increase RM productivity by 20%, enabling them to focus on more critical tasks and improve overall client engagement.
KPMG Clubhouse initiative aims to transform the staff lounge through technology and innovation, with the primary goal of boosting employee engagement and achieving “state-of-the-art” clubhouse.
The process began with interviews and journey mapping, revealing a need for more personalized experiences. The resulting innovative experience is derived through an end-to-end journey:
- Entrance: Staff enter the premises via facial recognition, allowing access even when their hands are full with laptops or personal belongings.
- Welcome: Upon entering, staff are greeted with personalized messages generated by predictive AI.
- Grab and Go: Quick and easy purchase of nutritious meals using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology ensures optimal convenience and efficiency.
- Rest & Relax: The lounge offers an “immersive experience” with ambiance dynamically adjusted through weather and time APIs, providing KPMG employees with a fresh and invigorating environment every time they enter.

Source: KPMG Clubhouse
All success stories highlight a common thread: true innovation emerges from a profound understanding of human needs and the strategic application of technologies like generative and predictive AI to elevate the overall experience. As Steve Jobs famously said, “You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work backward to the technology,” not the other way around.